Injection molding is a widely used process in the manufacturing of plastic products. It involves melting plastic pellets or granules and injecting them into a mold cavity to form the desired shape. The quality of the final product largely depends on how well the plastic melts and flows during the process. The melting behavior of plastics varies depending on their chemical composition and crystalline structure. Understanding the differences between melting amorphous and semi-crystalline plastics is crucial to obtaining melt uniformity and producing quality products.
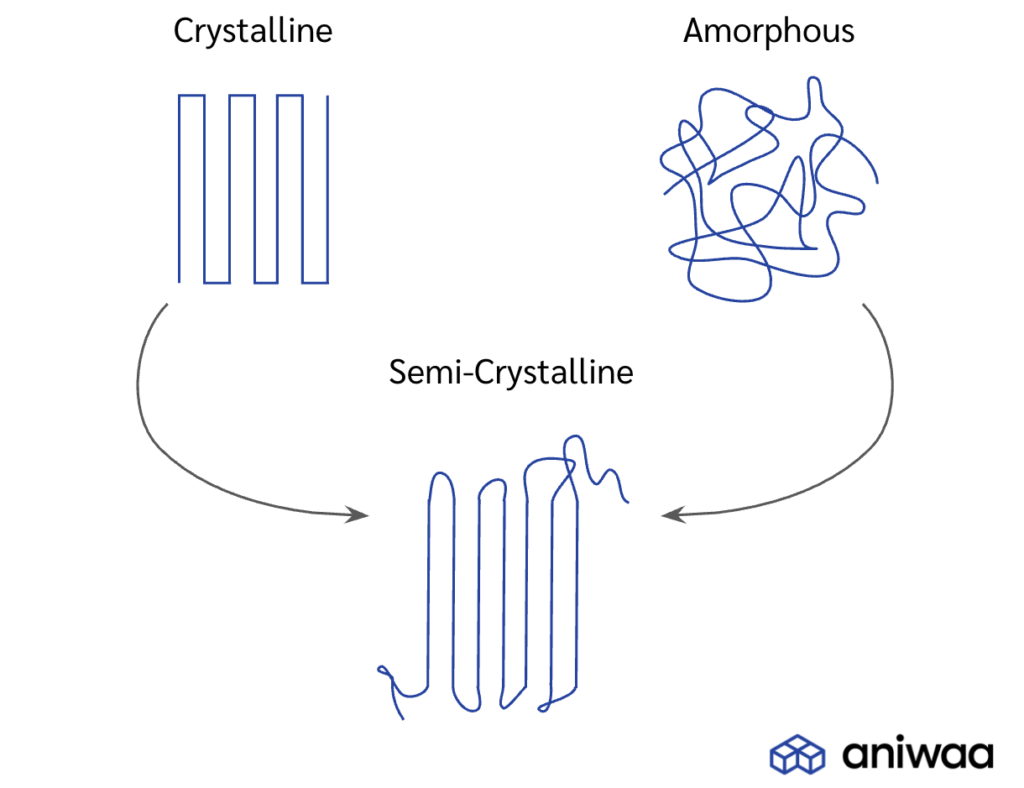
Amorphous plastics have a disordered molecular structure, which means that they do not have a distinct crystal lattice. Examples of amorphous plastics include polycarbonate, acrylic, and ABS. When amorphous plastics are heated, they soften gradually and pass through a temperature range known as the glass transition temperature (Tg). At Tg, the plastic changes from a rigid, glass-like state to a rubbery state, which allows it to flow easily. Above Tg, amorphous plastics continue to soften until they reach their melting temperature (Tm), at which point they become a viscous fluid. Amorphous plastics have a relatively low melting point and tend to melt uniformly without significant chemical degradation.
Semi-crystalline plastics, on the other hand, have a well-defined crystal structure, which means that they have regions of ordered molecular chains. Examples of semi-crystalline plastics include polyethylene, polypropylene, and nylon. Semi-crystalline plastics have both a melting temperature (Tm) and a crystallization temperature (Tc). When heated above Tc, these plastics start to melt, but only the amorphous regions melt at first. The crystalline regions remain solid until the temperature reaches Tm, at which point they start to melt as well. As a result, semi-crystalline plastics tend to have a more complex melting behavior than amorphous plastics. They also have a higher melting point and require higher processing temperatures.
Understanding the melting behavior of plastics is crucial in injection molding because it affects how the plastic flows inside the mold cavity. Good melt uniformity is essential for producing parts with consistent dimensions, surface finish, and mechanical properties. Achieving melt uniformity requires control over several process parameters, such as melt temperature, injection speed, packing pressure, and cooling time. The optimum settings for each parameter depend on the specific plastic being used, as well as the mold design and part geometry.
Shenzhen Zhongda Plastic Mould Co., Ltd. is a one-stop solution manufacturer based in China. Established in 2010 and located in Shenzhen Economic Development Zone, we offer multiple services, including product design, mold design, mold making, injection molding, and assembly. Our state-of-the-art injection molding equipment and experienced technicians enable us to produce high-quality plastic products precisely and cost-effectively. We have experience working with a wide range of plastics, including amorphous and semi-crystalline materials. We can help you select the right plastic for your product and optimize the injection molding process to ensure excellent melt uniformity. Contact us today to learn more about our services.